How to Tell if Your Child is Allergic to Milk
Because it’s one of the most common types of food allergies in children, a milk allergy should not come as a surprise to a new parent. According to FARE (Food Allergy Research & Education), approximately 2.5% of children under the age of three years old are allergic to milk. This condition – which is caused by the immune system’s abnormal reaction to milk protein – is most often associated with cow’s milk, though the milk of goats, sheep, and other domestic animals can cause reactions as well due to similarities in the proteins. Whatever the cause, it is important to know symptoms can range from mild (ex: hives) to severe (ex: anaphylaxis). It may be helpful for parents to know how to spot the signs of a reaction, as well as, what to do if they see these signs in their child. Here, the experts at Cambrooke will discuss how to tell if your child is allergic to milk and what you should do if they are; keep reading to learn more.
Signs That Your Child is Allergic to Milk
It is important to note that the symptoms of a milk allergy can vary in type and severity from child to child (and even between reactions in the same child). While the signs discussed below may be present in some form, it’s best not to assume that a simple rash or a runny nose is a definite indication that your child is allergic to milk. If you suspect that a milk allergy is to blame, talk to your child’s pediatrician or allergist, and let them guide you in determining if your child has a milk allergy. That said, the following are some of the most common signs that your child is allergic to milk.
Immediate Signs of a Milk Allergy
Any list of the symptoms of a milk allergy is best divided into two categories: immediate and delayed. Some children who are allergic to milk may exhibit the following issues right away, while others may not show any indication of a problem for hours or days. These are the immediate signs that will typically appears within minutes to a few hours after ingesting milk:
- Hives
- Swelling, especially around the mouth and throat
- Wheezing, coughing or other signs of respiratory distress
- Sneezing or runny nose
- Stomach pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea
In addition to the symptoms listed above, a milk allergy can also cause anaphylaxis – the term for a severe, potentially life-threatening reaction that can affect many areas of the body, including breathing and blood circulation. If after drinking milk or eating/drinking a product containing milk protein you notice signs that may indicate your child is having difficulty breathing such as: severely flushed in their face, coughing or wheezing, scratching at their face or mouth, turning blue or becoming unresponsive, it is recommended that you seek immediate emergency assistance. Please discuss with your child’s doctor or read here to learn more about how to manage an anaphylactic reaction.
Delayed Signs of a Milk Allergy
Even if your child displays very few or none of the immediate symptoms listed above, they may still be allergic to milk. Should your child show any of the following signs in the hours to days after consuming dairy products, it is important to discuss them with your child’s pediatrician about a possible milk allergy:
- Skin rash
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloody stool
- Acid reflux
- Chronic vomiting
- Colic (in infants)
Determining the cause of your child’s symptoms, with your pediatrician’s help, will allow you to develop a treatment plan to reduce or manage their symptoms.
How to Tell if Your Child is Intolerant or Allergic to Milk
Sometimes there can be a lot of overlap between the signs of a milk allergy and those of a milk intolerance, such as lactose intolerance. Despite the similarities, these conditions not only work in different ways, but they also require different treatments. With milk allergy, the immune system is having a negative response to the protein in milk. Lactose intolerance occurs when a person lacks enough of the enzyme needed to breakdown lactose, the sugar in milk.
For example, if your child is lactose intolerant then he or she may experience digestive issues, including an upset stomach, gas, bloating, or diarrhea, all of which typically happens within a few hours of eating or drinking milk products that contain lactose. A milk protein intolerance, on the other hand, usually occurs over a period of minutes to days after drinking milk, can affect many parts of the body and is not limited to gastrointestinal symptoms.
What to Do if Your Child is Allergic to Milk
Your pediatrician or allergist can help determine if your child is allergic to milk through testing or an elimination diet. Once a diagnosis is made, the next step is to find ways to keep your child nourished and healthy while avoiding milk protein. While a variety of products exist to support getting adequate nutrition, their effectiveness can vary based on the ingredients they use and the form of protein they include.
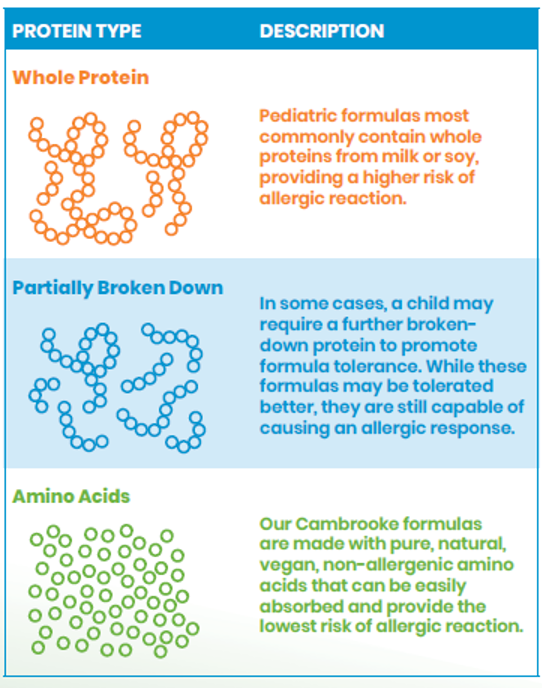
For instance, some formulas are made with whole or partially broken-down milk proteins, which may still trigger a reaction in a child with an allergy. By comparison, an amino acid-based formula is ideal for a child who is allergic to milk because these compounds can provide the same nutrition as other formulas without causing a harmful response by your child’s immune system.
Amino Acid-Based Formulas for Children Who Are Allergic to Milk
If your child is allergic to milk, know that it’s easier than ever to provide the complete nutrition your child needs to thrive. By including an amino acid-based formula designed for children 1 year of age or older, like Cambrooke’s EquaCare Jr. in your child’s diet, you can get the same nutrition offered by other brands at a more reasonable price or you could opt for our Essential Care Jr. formula, which provides an improved nutritional profile at a comparable price. Our premium formula, Essential Care Jr., is also a nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for children 1 year of age or older. It includes special features designed to support the entire body that are not contained in other formulas on the market. These unique features include vitamin K2 for stronger bones; low-FODMAP ingredients that may be easier to digest; and both DHA and lutein for brain development and eye health. To learn more about each of these options and how they can help children with a cow’s milk allergy, visit us online or call (833) 377-2773 today.



