How Our Formulas Help Those with Common Sensitivities and Digestive Conditions
Click on any of the conditions below to find out how Essential Care Jr. and EquaCare Jr. can help.
Severe Food Allergies
A food allergy occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to a usually harmless protein found in a food. Symptoms can occur when coming in contact with even a tiny amount of the food. Reactions can range from mild to severe and even potentially life threatening.
The top 8 food allergens are milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish & shellfish.
What are the symptoms of a food allergy?
Symptoms can include any of the following:
Skin: redness, itchy hives, rashes, or eczema
Respiratory: nasal congestions, runny nose, sneezing, dry cough, wheezing, asthma or shortness of breath, turning blue
Gastrointestinal (GI): nausea, vomiting, stomach cramping or diarrhea
Cardiovascular: drop in blood pressure, feeling faint, confused, weak or passing out, chest pain, weak pulse
Nervous systems: itchy mouth or ear canal, trouble swallowing, swelling of the lips, tongue and/or throat that blocks breathing
Reactions can occur immediately, or within a few minutes to hours. The scariest of these reactions is called Anaphylaxis which can be life threatening if not treated immediately with epinephrine.
How are food allergies diagnosed?
Tests should be conducted by a board certified allergist who will take into account your detailed history. Your primary care physician can provide you with a referral if needed. An allergist may use a combination of testing methods to confirm results.
If food allergy testing is negative, this is definitive. However, positive results are wrong 50% of the time. This is why it is ideal to only test the suspected food rather than a panel. An oral challenge is the gold standard of food allergy testing but are time consuming and place the patient at risk of having a reaction.
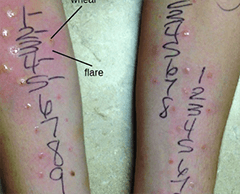
Skin Prick Test (SPT)
Procedure
- Tiny needles puncture the skin and a small amount of the food protein is applied
- The wheels around the reaction sites are then measured to identify a food allergy
Time for Test
- Results available in about 30 minutes
Limitations
- Can lead to over diagnosis because of high number of false positives
- Does not measure severity of reaction
- Not diagnostic alone
- Best used together with blood test
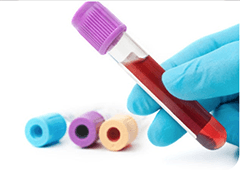
Serum IgE Test
Procedure
- Allergen specific blood test
- Must be drawn by or sent to lab for analysis
- Higher numbers = more accurate
Time for Test
- Results make take several days to a week
Limitations
- Can lead to over diagnosis because of frequent false positives
- Measurements vary by laboratory
- Not diagnostic on their own
- Best used together with skin test

Oral Food Challenge
Procedure
- Eliminate possible allergen for at least 2 weeks prior to test
- A very small measured dose of the suspected food is eaten and every 30 minutes the portion is gradually increased
- The patient will be supervised in the clinic for at least 2 hours or longer based on history after the last dose is finished
Time for Test
- Can take 4 to 8 hours per food
Limitations
- Must be conducted in a medical office with careful medical supervision and emergency medication/ crash cart ready
- Poses risk of reaction
- Increased cost of supplies needed
- Time needed to allow for possible reaction
- Fear of reaction by child or caregiver
What is the treatment for food allergies?
At this time the primary treatment for food allergies is complete avoidance of the allergen. This requires careful label reading to check for hidden allergens. The Food Allergy Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of 2004 (FALCPA) requires manufacturers to list the top 8 allergens even if it is only a trace amount.
For those with multiple allergens food avoidance can lead to a nutritionally incomplete diet. Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr. can be utilized to give additional calories and needed protein for growth as well as needed vitamins and minerals.
Will I ever be cured of my food allergy?
Unfortunately, there is no definitive answer. For those with allergies to eggs, milk, soy or wheat, these may eventually disappear over time. If you are allergic to peanuts, tree nuts, fish and shellfish, these tend to be a lifelong restriction.
Where can I learn more about food allergies?
The following sites have accurate information about the treatment of food allergies. They can also provide a information on where to find a board certified allergist near you.
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology: https://www.aaaai.org/
- American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology: https://acaai.org/
- Food Allergy Research & Education: https://www.foodallergy.org/
- Kids with Food Allergies: https://www.kidswithfoodallergies.org/

Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
What is EoE?
This is a chronic, allergic inflammatory disease of the esophagus that occurs when a type of white blood cell, the eosinophil, accumulates in the esophagus. This accumulation is triggered by the protein in foods. The increased number of eosinophils causes inflammation and damage to the esophagus. This damage may make eating difficult or uncomfortable, potentially resulting in poor growth, chronic pain and/or difficulty swallowing. Some cases of EoE can require the elimination of multiple food proteins. Amino acid formulas, like Essential Care Jr. and EquaCare Jr., may be necessary to ensure nutritional needs are satisfied.
What are the symptoms of EoE?
Infants & Toddlers:
- Reflux-like symptoms
- Vomiting
- Delayed transition to solid food or advancing to textures appropriate for age
- Vitamin and/or mineral deficiencies
- Poor growth
School Age:
- Vomiting & pain
- Feeding refusal
- Poor growth
- Vitamin and/or mineral deficiencies
Adolescents & Adults:
- Swallowing difficulty, chest pain, food impaction & upper abdominal pain
- Vitamin and/or mineral deficiencies
- Food avoidance
- Underweight
How is EoE diagnosed?
- A gastroenterologist needs to evaluate and assess symptoms.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause similar symptoms so must be ruled out.
- An endoscopy procedure must be performed for diagnosis. This procedure requires sedation, and a small tube called an endoscope is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus. A small tissue sample, called a biopsy, is taken of the esophagus. The sample is then checked for number of eosinophils. If the count is 15 or more eosinophils seen under a high-powered microscope, this is classified as EoE.
Empiric Elimination
- Patients eliminate common food allergens and gradually reintroduce
- Six-Food Elimination:
- Milk, eggs, wheat, soy, peanuts/tree nuts, fish/shellfish
- Has been shown to reduce eosinophils in the tissue in up to 75% of patients
- Four-Food Elimination:
- Milk, wheat, egg, soy/legumes
- Two-Food Elimination:
- Milk & wheat
Testing Directed Elimination Diet
- Foods that test positive on allergy testing like Skin Prick Testing (SPT) & Atopy Patch Testing (APT) are removed from the diet
- SPT: Examines immediate hypersensitivity to food antigens
- APT: A diagnostic tool with high predictive capacity for late-phase clinical reactions
- The positive food allergies as well as cow’s milk are typically eliminated due to milk’s poor negative predictive value on testing
Elemental Diet
- The patient drinks only an amino acid based formula, like Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr.
- Sometimes a feeding tube may be required
- Reduces eosinophils in up to 90% of patients with symptom improvement in as early as 2 weeks
Are there medicines for EoE?
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
- These are acid suppressors and they may also relieve symptoms in some patients
- Induce remission in a proportion of patients with EoE
- If treatment is stopped, eosinophilia recurs in 3-6 months
Topical Steroids
- Often successful to control inflammation, suppress the eosinophils, and put EoE into remission
- Topical steroids (fluticasone or budesonide) are swallowed from an asthma inhaler or mixture
Will I ever be cured of my EoE?
- Eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic condition. Those with EoE will need ongoing monitoring and management.
- If EoE goes untreated, esophageal narrowing (strictures) can occur and this could cause a food impaction. It can also make eating very difficult and uncomfortable.
- EoE can be overwhelming for the child and family; however, it is important to focus on other positive activities that don’t relate to food. If the condition is treated correctly, those with EoE can lead a normal life.
Where can I learn more about EoE?
The following sites have accurate information about the treatment of EoE. They can also provide information on where to find a doctor specializing in EoE treatment near you.
American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI): https://www.aaaai.org/conditions-and-treatments/related-conditions/eosinophilic-esophagitis
American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI): https://acaai.org/allergies/types/food-allergies/types-food-allergy/eosinophilic-esophagitis
American Partnership for Eosinophilic Disorders (Apfed): https://apfed.org/about-ead/egids/eoe/
Kids with Food Allergies: https://www.kidswithfoodallergies.org/eosinophilic-esophagitis-eoe.aspx
Food Protein Intolerance
There is no medical testing for a non-IgE mediated food allergy, unlike classic IgE mediated food allergy. This can be frustrating due to the inability to confirm a specific food protein allergen to be avoided. Adding an amino acid formula, like Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr., can provide a sense of relief in knowing that there is no exposure to the food protein, while ensuring a more balanced diet.
Non-IgE Mediated Food Allergy
- A food protein intolerance is also known as a non-IgE mediated food allergy.
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) are a form of specialized proteins called antibodies produced by the immune system.
- A non-IgE mediated response to a food protein is related to a different immunologic mechanism that remains unknown.
- Non-IgE mediated food allergic disorders are a well-established clinical category of food allergy, and they mostly affect the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diagnosis of a non-IgE mediated food allergy relies on oral food challenges as there are no skin or blood tests for diagnosis.
- These allergies are managed experimentally with food avoidance.
- An Amino Acid formula, like Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr., may provide support with the restrictive diets needed for these disorders if they continue into childhood.
Food Protein–Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP)
A benign condition in which about 60% of cases occur in breast-fed babies, and may resolve by mother eliminating milk and soy from her diet. The remainder occurs in infants who are fed cow’s milk or soy protein-based formulas.
- Symptoms: bloody stools in well-appearing infants that begins between 1 and 4 weeks of age
- Common foods to avoid: milk and soy
- Diagnosis: because it is a non-IgE mediated allergy, there is no blood or skin testing available for diagnosis
- Treatment: strict avoidance of milk and soy
- Most formula fed infants are changed to an amino acid formula designed for infants
- Resolution: a majority have resolution of symptoms by 12 months of age and can then consume milk and soy without problems
Milk Soy Protein Intolerance (MSPI)
MSPI is a temporary reaction to the proteins found in cow’s milk and soy products. You may also see it referred to as food protein-induced colitis or cow’s milk protein intolerance (CMPI). Symptoms can appear as early as 2-3 weeks after birth.
- Symptoms: colic, irritability/fussiness, weight loss, congestion, repeated vomiting, reflux and sometimes skin rashes or blood or mucus in the stools
- Common foods to avoid: milk and soy
- Diagnosis: because it is a non-IgE mediated allergy, there is no blood or skin testing available for diagnosis
- Treatment: strict avoidance of milk and soy
- If mother is breast feeding – she should avoid milk and soy in her diet
- Most formula fed infants are changed to an amino acid formula designed for infants
- Resolution: a majority have resolution of symptoms by 12 months of age and can then consume milk and soy without problems
Food Protein–induced Enteropathy (FPE)
- Symptoms: intermittent vomiting or diarrhea following consumption of the food protein trigger, bloody stools are rare
- Common foods to avoid: milk and soy
- Diagnosis: because it is a non-IgE mediated allergy, there is no blood or skin testing available for diagnosis
- Treatment: strict avoidance of the triggering food. If symptoms remain after the first year of life, supplementation with an amino acid formula, like Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr., may help.
- Resolution: Most cases resolve in 24-36 months
Food Protein–Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (FPIES)
FPIES is often misdiagnosed early on as a potential severe blood infection or repeated infections of a gastrointestinal virus.
- Symptoms: decrease in energy, change in body temperature, severe vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration or low blood pressure leading to
hospitalization - Common foods to avoid: cow milk, soy and grains like rice, barley, and oats
- Diagnosis: because it is a non-IgE mediated allergy, there is no blood or skin testing available for diagnosis
- Treatment: strict avoidance of the triggering food and possible supplementation with an amino acid formula, like Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr.
- Resolution: Most children outgrow FPIES by 3 or 4 years of age
Where can I learn more about Non-IgE Food Intolerances?
The following sites have accurate information about the treatment of the Non-IgE food intolerances reviewed above. They can also provide information on where to find a board certified allergist near you that specializes in treatment of these conditions.
MSPI: Complete Children’s Health https://www.completechildrenshealth.com/what-is-mspi/
FPIES: The FPIES Foundation http://fpiesfoundation.org/about-fpies-3/
Kids with Food Allergies https://www.kidswithfoodallergies.org/food-protein-induced-enterocolitis-syndrome-fpies.aspx


Malabsorptive Syndromes
Malabsorption occurs when people are unable to absorb nutrients from what they eat, like carbohydrates, fat, protein, vitamins and/or minerals. This may cause excessive stools, GI symptoms and eventually nutritional deficiencies. Ingredients that help improve absorption include amino acid proteins and medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are easy-to-absorb sources of protein and fat. That’s why we use pharmaceutical grade, naturally fermented amino acids and have 35% of MCT fat calories in Essential Care Jr. and 33% of MCT fat calories in EquaCare Jr.
Phases of digestion and absorption
When any of these phases are altered, this can result in malabsorption.
- First, enzymes break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Fat requires bile salts for further break down in this phase.
- Next, there is further digestion by enzymes in the brush border of the intestines. After complete breakdown, there is uptake by the intestines of the broken down end-products.
- Finally, the nutrients are then transported to tissues throughout the body.
What are the possible causes of Malabsorption Syndrome?
There are 8 major causes of malabsorption:
- Cardiovascular Disorders: congestive heart failure, constructive pericarditis or mesenteric vascular insufficiency
- Drug-induced Disorders: cholestyramine, colchicine, irritant laxatives, neomycin or phenindione
- Impaired Digestion: gastric surgery or gastrinoma
- Inadequate Absorptive Surface: jejunoileal bypass or short bowel syndrome
- Infection: acute infectious enteritis, parasitic infections, tropical sprue or Whipple’s disease
- Intestinal Mucosal Abnormalities: amyloidosis, Crohn’s disease, cystinuria, eosinophilic enteritis or non-tropical sprue
- Lymphatic Obstruction: intestinal lymphoma, lymphangiectasis or tuberculosis
- Reduced Bile Salt Concentration: bacterial overgrowth, ileal resection or liver disease
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Malabsorption?
With so many reasons that can cause malabsorption, the symptoms can vary according to the severity of condition and how long the person has the disorder
- Bloating or stomach distention
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fatty stools
- Gas
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Stomach cramping
- Weight loss
How is Malabsorption Diagnosed?
In addition to looking at your medical history, a doctor will ask questions about symptoms, and what makes them better or worse.
- Testing might include:
- Blood tests: blood count, electrolytes and protein levels
- Stool tests: looking for excess fat
- Breath tests: looks for hydrogen gas that is produced with lactose intolerance and malabsorption of other carbohydrates
- Imaging: looking at the structure of the GI tract
- Scoping: upper GI or lower GI to visualize the intestinal lining and take biopsies
What is the treatment of Malabsorption?
- Treatment will depend on the cause of the malabsorption.
- Initially, diet restriction of any offending foods like lactose or gluten will be the first step.
- If nutrient deficiencies are found, an amino acid formula like Essential Care Jr or EquaCare Jr may be suggested to correct the problem.
- Medications to replace missing enzymes or enhance appetite may be prescribed.
- Frequent follow-up appointments with the doctor and possibly a dietitian will be needed to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
Is there a cure for Malabsorption Syndrome?
- Most Malabsorption disorders are chronic life-long conditions that require ongoing medical treatment.
- With proper medical treatment and diet changes, many with malabsorption can have normal lives.
- Your doctor may recommend monitoring body weight to ensure you are receiving adequate nutrition.
- Call your doctor if symptoms like diarrhea, fatty stools or weight loss occur.
Where can I learn more about Malabsorption Syndrome?
The following sites have accurate information about the treatment of malabsorption. They can also provide information on where to find a Gastroenterologist specializing in treatment near you.
International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders: https://iffgd.org/other-disorders/malabsorption.html
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (FPIES)
An FPIES reaction can be scary and it is something no parents ever want their child to experience. Parents can take comfort in knowing our complete amino acid-based formulas are free of proteins that could trigger an FPIES reaction. We also know that the diet of a child with FPIES can be very limited due to the inability to introduce food groups quickly. Our Essential Care Jr. and EquaCare Jr. are both nutritionally complete formulas and designed to meet 100% of children’s nutrition needs.
FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting, diarrhea and dehydration. Reactions are triggered by eating a certain food protein. The most common food triggers are cow milk, soy and grains. Of the grains, rice, barley, and oats are most likely to cause a reaction. A severe case of FPIES can result in an energy decrease, change in body temperature and low blood pressure leading to hospitalization. FPIES is often misdiagnosed early on as a potential severe blood infection or repeated infections of a gastrointestinal virus.
Symptoms
FPIES symptoms are most likely to start after the introduction of milk or soy-based formulas. Older infants can have a reaction with the first introduction of solid foods around 4 months of age. This usually occurs when the infant is introduced to rice, oats, barley and other similar foods.
FPIES reactions involve the gastrointestinal tract. Vomiting and diarrhea may not occur until several hours after the food protein is consumed and it may be difficult to evaluate the trigger food due to the delayed reaction.
Diagnosis
When a child with FPIES is taken to a hospital, it is often misdiagnosed as a bacterial infection (sepsis) or gastrointestinal viral illness. Because FPIES is a non-IgE mediated allergy, it cannot be diagnosed with a skin or blood test. FPIES is typically diagnosed using the child’s clinical history and symptoms.
In some cases, a clinically supervised oral food challenge is needed to confirm FPIES. It may be necessary to find a solid food that a child can tolerate to ensure he or she is developing with oral feeding skills. An oral food challenge may also be helpful in determining whether a child has outgrown FPIES.
Management and Treatment
- Management of FPIES requires the removal of the trigger food from the diet.
- If the FPIES reaction is to milk/soy formula, a hypoallergenic formula may be necessary. If the FPIES reaction is to solid foods, the allergist may suggest introducing low risk fruits and vegetables rather than cereals and grains.
- In the most extreme cases, children with FPIES can require hospitalization for IV hydrations and possibly treatment with anti-vomiting medication.
Short Bowel Syndrome
What causes Short Bowel Syndrome?
Short Bowel Syndrome is caused by the surgical removal of part of the small intestine and sometimes part of their large intestine. Those with
short bowel syndrome experience significate damage of the small intestine or may suffer from poor motility (movement) of the intestines. Common causes include:
Congenital birth defects
- Intestinal atresia
- Gastroschisis
- Hirschprung’s disease
Disease or trauma
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
- Intestinal malrotation with volvulus
- Hernias and intussusception
- Abdominal tumors and radiation
- Crohn’s disease
What are the symptoms of Short Bowel Syndrome?
The severity of symptoms and malabsorption can be determined by the remaining length and location of the resection.
The symptoms of Short Bowel Syndrome can be:
- Bacterial overgrowth
- Diarrhea
- Dumping syndrome
- Malabsorption
- Fluid and electrolyte disturbances
- Malnutrition
- Weight loss
How is Short Bowel Syndrome Treated?
- The treatment of Short Bowel Syndrome will depend on the amount of intestine that was removed and the location within the bowel.
- For those that can tolerate receiving nutrition through the GI tract, they may need an amino acid formula like Essential Care Jr. or EquaCare Jr. in order to meet their nutrition needs with fewer symptoms.
- Because the protein in these formulas is in the most simple form of amino acids, it is readily absorbed with no digestion required
- MCT is a fat that can be absorbed without the need for enzymes, so the higher levels of MCT in Essential Care Jr. may be beneficial
- Some children with Short Bowel Syndrome may need to receive all of their nutrition by an IV, commonly called Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
Will I ever be cured of Short Bowel Syndrome?
- Unfortunately, Short Bowel Syndrome is a chronic condition because parts of the intestine are surgically removed.
- The small intestines are made up of three sections; the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum.
- The duodenum and jejunum are the main sites for carbohydrate, protein, fat and mineral absorption.
- The ileum is the only site for vitamin B12 and bile salt absorption.
- The ileum can adapt and compensate for loss in the jejunum. However, the duodenum and jejunum cannot take on the absorptive functions of the ileum.
- If part of the large intestine (colon) is also removed, there can be increased symptoms of diarrhea, electrolyte losses, bacterial overgrowth and malabsorption of fat.
Where can I learn more about Short Bowel Syndrome?
The following sites have accurate information about the treatment of Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS). They can also provide information on where to find a Gastroenterologist specializing in SBS treatment near you.
National Institute of Health (NIH): https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/short-bowel-syndrome
Short Bowel Foundation: http://shortbowelfoundation.org/
Short Bowel Syndrome: https://www.shortbowelsyndrome.com/sbs-support/connect-with-others
Short Gut Syndrome families’ support group: http://www.shortgutsupport.com/
Corn Sensitivities
Most hypoallergenic amino acid formulas use corn syrup solids as the main source of carbohydrate. Those with corn sensitives may wish to avoid corn syrup solids that are the #1 ingredient in all amino acid formulas other than Essential Care Jr. The corn syrup found in other formulas is most commonly derived from corn starch that has been highly processed to remove corn protein per the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology (ACAAI).
Protein is known to be the part of food that the body reacts to with a food allergy. Although the refinement of the corn starch removes a majority of the protein, a product cannot be guaranteed free of the protein unless it has been tested for that particular protein. It has been noted by some medical providers that there are reports from patients and families of reactions to the corn syrup despite reported protein removal through refinement. This may be due to the undetectable amounts of corn protein that may be found in the highly refined corn syrup or it may be related to a sensitivity to the carbohydrate. Because Essential Care Jr. uses tapioca as its carbohydrate source it may be a good alternative to other amino acid-based formulas that use corn syrup solids as the primary carbohydrate source.

When Allergies Continue Beyond Infancy
Though the majority of infants with a cow’s milk allergy will outgrow the sensitivity by his or her first birthday, it is common to remain intolerant to the protein well beyond 1 year of age. Using an amino acid formula can ensure your child receives all of the nutrients that he or she needs without being exposed to potential allergens.
An Amino Acid Formula that is More Gentle on the Digestive System
Finding that perfect formula that soothes your child’s digestive condition can be a long and difficult process. While some illnesses can be addressed through common allergen-free products, others require a milder touch. Because our products are delicately formulated to be gentle on the system while providing complete nutrition, Essential Care Jr. and EquaCare Jr. can be counted on to help with an array of gastrointestinal conditions.
Find Out What Makes Our Formulas So Special
Finding healthy, wholesome nutrition for a child with severe allergies shouldn’t be hard. By offering products with broad nutritional value at affordable prices, we make it easier to provide for your child’s dietary needs without risking exposure to harmful allergens. Try one of our products today and see for yourself how they may improve your child’s quality of life.

